T pipe fittings in water treatment systems face significant corrosion challenges. The aggressive nature of treated water and various chemical additives makes these components highly susceptible. Corrosion resistance is a critical factor for system longevity and efficiency. This post explores primary corrosion challenges and effective solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right material for T pipe fittings. Stainless steel, plastic, or special metals can stop rust.
- Use coatings or linings on T pipe fittings. These layers protect the metal from water and chemicals.
- Control water chemistry and use good design. This helps T pipe fittings last longer and work well.
Understanding Corrosion Challenges for T Pipe Fittings
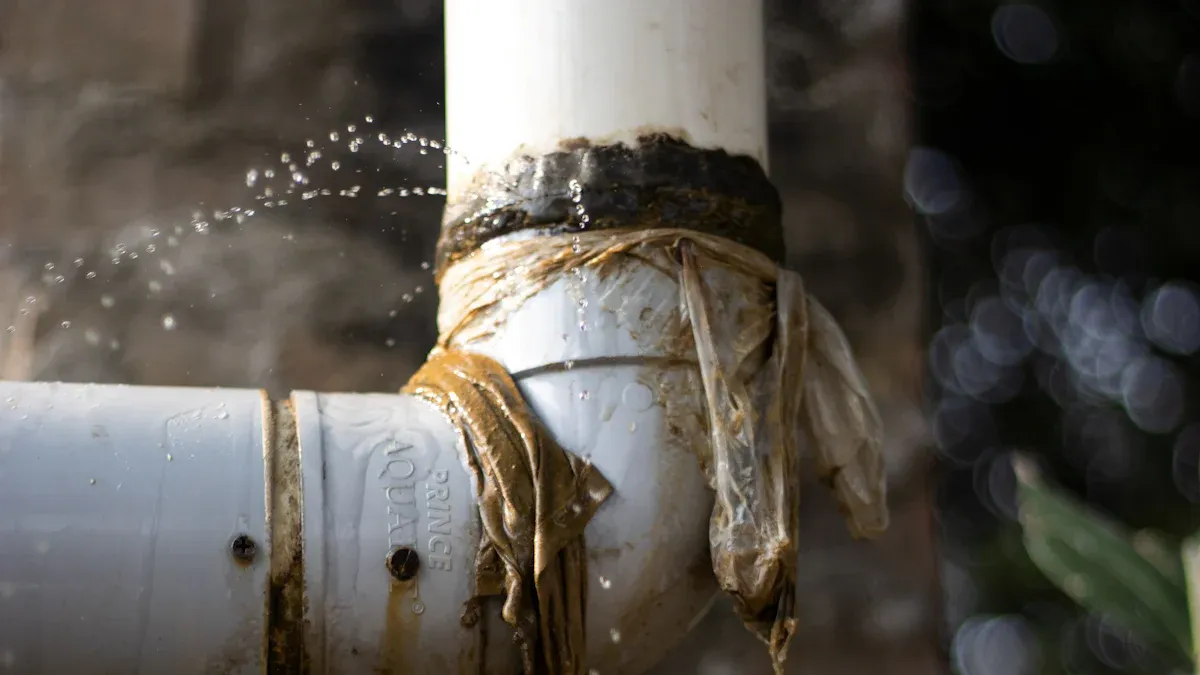

Common Corrosion Types Affecting T Pipe Fittings
Water treatment systems expose T pipe fittings to various corrosive environments. Pitting corrosion is a common issue. It creates small holes or pits on the metal surface. Crevice corrosion occurs in confined spaces, like under gaskets or in joints. These areas trap stagnant water, which becomes more corrosive. Galvanic corrosion happens when two different metals connect in an electrolyte. One metal corrodes faster than the other. Stress corrosion cracking can also affect fittings. It occurs when tensile stress and a corrosive environment combine.
Factors Accelerating Corrosion in Water Treatment T Pipe Fittings
Several factors increase corrosion rates in water treatment systems. Water chemistry plays a significant role. Low pH (acidic water) or high pH (alkaline water) can accelerate material degradation. High temperatures also speed up chemical reactions, including corrosion. Dissolved oxygen in the water acts as an oxidizer, promoting corrosion. The presence of chlorides, sulfates, and other aggressive ions further intensifies corrosive attacks. Flow velocity also impacts corrosion. High flow can cause erosion-corrosion, while low flow can lead to stagnant conditions.
Consequences of Corrosion in T Pipe Fittings
Corrosion in T pipe fittings leads to serious operational problems. It causes leaks, resulting in water loss and potential damage to surrounding equipment. Corroded fittings reduce system efficiency. They can restrict flow or contaminate the treated water with corrosion byproducts. This contamination compromises water quality. Ultimately, corrosion increases maintenance costs and shortens the lifespan of the entire water treatment infrastructure. Unplanned downtime for repairs also disrupts operations.
Material Selection for Corrosion-Resistant T Pipe Fittings
Choosing the right material for T pipe fittings is crucial for preventing corrosion in water treatment systems. Different materials offer varying levels of resistance to corrosive agents and environmental conditions. Engineers select materials based on water chemistry, temperature, pressure, and cost.
Stainless Steel T Pipe Fittings (304, 316, Duplex)
Stainless steel is a popular choice for many water treatment applications due to its inherent corrosion resistance. Different grades offer specific advantages.
- 304 Stainless Steel: This grade provides good general corrosion resistance. It works well in fresh water applications without high chloride levels. However, 304 stainless steel can be susceptible to pitting corrosion in environments with higher chloride concentrations.
- 316 Stainless Steel: This grade contains molybdenum, which significantly improves its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich environments. Water treatment plants often use 316 stainless steel for its enhanced durability in more aggressive conditions.
- Duplex Stainless Steel: Duplex stainless steels combine properties of both austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. They offer superior strength and excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking and pitting. Duplex grades are suitable for highly demanding water treatment processes where standard stainless steels might not suffice.
Non-Metallic T Pipe Fittings (PVC, CPVC, HDPE, FRP)
Non-metallic materials are excellent alternatives to metals, especially where chemical resistance is a primary concern. They do not corrode in the same way metals do.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC is a cost-effective material with good chemical resistance to many acids, alkalis, and salts. It is widely used for cold water applications in water treatment.
- CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride): CPVC offers similar chemical resistance to PVC but can withstand higher temperatures and pressures. This makes it suitable for hot water lines or processes requiring elevated temperatures.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): HDPE is known for its flexibility, toughness, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. It is often used for large diameter pipes and underground installations due to its durability and ease of fusion welding.
- FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic): FRP provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio and superior corrosion resistance to a wide range of chemicals. Manufacturers customize FRP for specific chemical environments, making it ideal for aggressive water treatment chemicals.
Exotic Alloy T Pipe Fittings (Hastelloy, Titanium, Tantaline®)
For extremely aggressive water treatment environments, exotic alloys provide the highest level of corrosion resistance. These materials come at a higher cost but offer unmatched performance in challenging conditions.
- Hastelloy: This nickel-based alloy offers exceptional resistance to strong acids, chlorides, and other highly corrosive chemicals. Water treatment facilities use Hastelloy in processes involving highly concentrated chemicals or extreme temperatures.
- Titanium: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, especially in oxidizing environments and chloride solutions. Its strength and lightweight properties make it valuable for specialized applications, such as desalination plants.
- Tantaline®: Tantaline® is a surface treatment that applies a thin, dense layer of tantalum to a base metal. This creates a highly corrosion-resistant surface, combining the strength of the base metal with the chemical inertness of tantalum. It provides protection against virtually all acids and corrosive media.
Material Compatibility for Mixed System T Pipe Fittings
When designing water treatment systems, engineers often use different materials for various components. Ensuring material compatibility is critical to prevent accelerated corrosion. Galvanic corrosion is a significant risk when two dissimilar metals connect in an electrolyte, such as water. The less noble metal acts as the anode and corrodes preferentially. The more noble metal acts as the cathode and receives protection. The severity of this corrosion depends on the potential difference between the metals, the ratio of cathodic to anodic surface areas, and the electrolyte’s conductivity.
For example, connecting stainless steel T pipe fittings to copper piping in water treatment systems creates a galvanic couple. Stainless steel is generally more noble than copper. This means copper becomes the sacrificial metal when these two materials connect. The copper will corrode faster than it would on its own. Designers must carefully consider the galvanic series of metals and use dielectric unions or other isolation methods to prevent direct electrical contact between dissimilar metals. This protects the less noble material from rapid degradation.
Protective Coatings and Linings for T Pipe Fittings
Protective coatings and linings offer an additional layer of defense against corrosion for T pipe fittings in water treatment systems. These barriers separate the fitting material from the corrosive environment. They extend the service life of components and reduce maintenance needs.
Epoxy Coatings for T Pipe Fittings
Epoxy coatings provide a robust solution for corrosion protection. These thermosetting polymer coatings form a hard, durable film on the internal and external surfaces of T pipe fittings. They create an impermeable barrier. This barrier prevents direct contact between the metal and corrosive water or chemicals. Epoxy coatings offer excellent adhesion to various substrates. They resist a wide range of acids, alkalis, and solvents commonly found in water treatment processes. Applicators can apply epoxy coatings through spraying, brushing, or dipping. The curing process forms a tough, smooth surface. This surface also reduces friction and prevents the buildup of deposits. However, epoxy coatings can become brittle at very low temperatures or soften at very high temperatures.
Polyurethane Linings for T Pipe Fittings
Polyurethane linings offer flexibility and superior abrasion resistance compared to many other coatings. These linings consist of a polymer material. They form a resilient and elastic layer on the interior of T pipe fittings. This elasticity allows the lining to withstand minor pipe movements or impacts without cracking. Polyurethane linings also provide excellent chemical resistance. They protect against many aggressive substances present in water treatment. Their smooth surface minimizes friction loss and inhibits microbial growth. Installers often apply polyurethane linings as a spray or cast-in-place material. They are particularly effective in applications where erosion from suspended solids is a concern.
Cement Mortar Linings for Large Diameter T Pipe Fittings
Cement mortar linings are a traditional and cost-effective method for protecting large diameter T pipe fittings and pipelines. Workers apply a layer of cement-rich mortar to the interior surface. This lining creates a physical barrier. It separates the metal from the water. The alkaline nature of the cement also passivates the steel surface. This passivation helps prevent corrosion. Cement mortar linings effectively prevent tuberculation, a form of corrosion that creates rust nodules. These nodules restrict flow. They also maintain water quality by preventing metal leaching. While highly durable for water transport, cement mortar linings can be susceptible to cracking from pipe deflection or aggressive acidic water. They are less common for smaller T pipe fittings due to application challenges.
Fluoropolymer-Lined T Pipe Fittings (PTFE, PFA)
Fluoropolymer linings, such as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA), offer the highest level of chemical resistance. These materials are virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals. They withstand extreme temperatures. Manufacturers bond a layer of PTFE or PFA to the internal surface of metallic T pipe fittings. This creates a non-stick, highly corrosion-resistant barrier. Fluoropolymer linings are ideal for handling highly aggressive acids, strong bases, and high-purity water applications. Their non-porous surface prevents contamination and minimizes product adhesion. While more expensive than other lining options, their exceptional performance in the most demanding water treatment environments justifies the cost. They ensure long-term integrity and prevent costly failures.
Corrosion Inhibition Strategies for T Pipe Fittings
Effective corrosion inhibition strategies are vital for extending the lifespan of T pipe fittings in water treatment systems. These methods actively prevent or slow down the degradation process.
Chemical Inhibitors for T Pipe Fittings
Chemical inhibitors introduce substances into the water stream. These substances form a protective layer on the metal surface of T pipe fittings. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing corrosive agents from reaching the metal. Common types include film-forming inhibitors, which create a physical film, and passivating inhibitors, which promote the formation of a stable oxide layer. Water treatment plants carefully select inhibitors based on water chemistry and the specific metals present. Proper dosing ensures effective protection without compromising water quality.
Cathodic Protection for Metallic T Pipe Fittings
Cathodic protection is an electrochemical method. It makes the metallic T pipe fittings the cathode of an electrochemical cell. This prevents corrosion. Two main types exist: sacrificial anode systems and impressed current systems. Sacrificial anodes, made from more active metals like magnesium or zinc, corrode instead of the fitting. Impressed current systems use an external power source to drive a current through inert anodes, protecting the fitting. Engineers often apply cathodic protection to large metallic structures and buried pipelines.
Water Chemistry Control for T Pipe Fittings Longevity
Controlling water chemistry directly impacts corrosion rates. Operators monitor and adjust several key parameters. Maintaining an optimal pH range prevents both acidic and alkaline corrosion. Reducing dissolved oxygen levels minimizes oxidative corrosion. Controlling alkalinity and hardness can form a protective scale on pipe surfaces. Limiting chloride concentrations also reduces pitting and crevice corrosion. Regular monitoring and precise chemical dosing ensure the water remains less aggressive towards the pipe materials. This proactive approach significantly extends the service life of the entire system.
Design and Installation Best Practices for T Pipe Fittings
Proper design and installation significantly extend the life of water treatment systems. These practices prevent premature failure and reduce maintenance costs.
Minimizing Stagnant Areas in T Pipe Fitting Design
Designers must eliminate stagnant zones within piping systems. Stagnant water promotes localized corrosion and microbial growth. These conditions accelerate material degradation. Engineers should use smooth transitions and avoid dead legs or unused branches. Proper flow dynamics ensure continuous water movement through all sections. This minimizes sediment accumulation and chemical concentration.
Proper Jointing Techniques for T Pipe Fittings
Correct jointing is crucial for system integrity. Technicians must follow manufacturer guidelines for all connections. Welding, threading, and flanging are common methods. Each technique requires specific tools and expertise. Proper alignment and sealing prevent leaks and crevice corrosion. Inadequate jointing creates weak points susceptible to failure.
Stress Reduction During T Pipe Fitting Installation
Installation practices directly impact fitting longevity. Installers must reduce mechanical stress on components. They should use adequate pipe supports to distribute weight evenly. Expansion joints accommodate thermal movement. Proper alignment of pipes before connection prevents undue strain on T Pipe Fittings. Excessive stress can lead to cracking or premature fatigue.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance of T Pipe Fittings
Ongoing inspection and maintenance are essential. Operators should schedule routine checks for all fittings. They look for signs of leaks, corrosion, or wear. Early detection of issues prevents major system failures. Regular cleaning and replacement of worn components ensure continuous, efficient operation. Proactive maintenance extends the service life of the entire system.
Effective corrosion resistance in T pipe fittings for water treatment demands a comprehensive strategy. This strategy combines careful material selection, suitable protective measures, and robust design. It also includes diligent maintenance practices. These elements collectively ensure system integrity and longevity, preventing costly failures and downtime.
FAQWhat is the most common type of corrosion in water treatment T pipe fittings?
- Pitting and crevice corrosion frequently affect T pipe fittings. Galvanic corrosion also occurs when dissimilar metals connect. These types degrade fitting integrity.
Which non-metallic materials offer good corrosion resistance for T pipe fittings?
- PVC, CPVC, HDPE, and FRP are excellent non-metallic choices. They resist many chemicals and do not corrode like metals. These materials suit various applications.
How do chemical inhibitors protect T pipe fittings from corrosion?
- Chemical inhibitors form a protective layer on the metal surface. This barrier prevents corrosive agents from reaching the fitting. They extend the component’s lifespan.
Media Contact
Company Name: Ningbo Fenghua Metal Products Co., Ltd.
Email: Send Email
Phone: 0086-13968334411
Address:Huangtan Town, Ninghai County
City: Ningbo
State: Zhejiang
Country: China
Website: https://www.nbfh-metal.com/